SS猜想:SU-76I太强势难逃被替换的命运
|
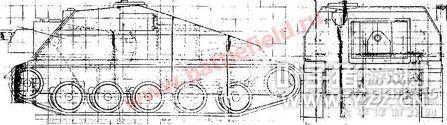
you probably heard about the screwup with the SU-76I. It did put Wargaming into an uncomfortable situation – now that it’s out, they can’t nerf it (it’s a premium tank after all), all the while the vehicle in the game is clearly overpowered. And so, they will have to introduce another lowtier tank destroyer to replace it I guess. And what do you know – there are two perfect candidates for the role, the SU-74 and SU-57b (the third one would be OP I guess). 你可能听说了被搞的一团糟的SU-76I,这让WG很尴尬---因为它是金币车,所以不敢挫它,但是它在游戏里又太强势、所以我猜他们有可能引入另一部低级TD来替换76I---有两个很不错的候选:SU-74和SU-57b(后者可能略OP)。 In the summer of 1943, the designers of the GAZ plant under the leadership of N.A.Astrov (famous Soviet vehicle designer, responsible for example for the T-60, T-70, T-80 or SU-76M) created two light tank destroyer projects and offered them to the national commissariat of tank industry under the designation of GAZ-74. 在1943年夏天,在N.A.Astrov(苏联著名坦克设计师,T-60,T-70,T-80或是SU-76M都出自他之手)领导下的GAZ厂设计师们开发出了2个轻型坦克歼击车项目,并以GAZ-74的代号呈递给国家坦克工业军需部审查。 The first vehicle (GAZ-74a) project resembled the already existing SU-76, while the other (GAZ-74b) was more of a “Hetzer” design, with closed compartment and frontal gun. Where the first vehicle was relatively tall (albeit maneuverable), the second one was low and sleek, well armored (frontal armor was 35mm thick, but it was sloped) and it was armed with a 76mm S-1 gun, the same type used on the SU-76I. It was to be powered by a lend-lease diesel engine by General Motors, the 110hp GMC-71, that was to be license-produced in the USSR by the YaMZ plant in Yaroslavl. 第一个项目(GAZ-74a)模仿了现有的SU-76,而另一个(GAZ-74b)设计则更像“追猎者”---封闭战斗室,主炮前置。第一个坦克相对较高(更利于操纵),第二个则外形低矮整洁,拥有不错的防护(前装甲虽然只有35mm,但是有着不错的倾角),装备一门76mm S-1主炮,和SU-76I上的一样。74b型由一台通过租借法案泊来的通用汽车公司的GMC-71柴油机驱动,功率为110马力。该引擎在获得生产许可后在苏联雅罗斯拉夫尔的YaMZ厂生产。 Design-wise, the project turned out to be a mashup of T-70 parts and equipment (the vehicle was based on the T-70) and the American engine with some new development added into the mix. Generally, the vehicle resembled the famous German “Hetzer”, although when it comes to its gun and armor, it was inferior to it. The suspension was taken from the T-70 as well, with individual torsion bars for each of the 5 roadwheels and 4 return rollers. 设计方面,74b型实际上就是T-70的各种零部件,美国发动机以及一些在设计过程中的新技术的杂糅。总体来说,尽管在火炮和装甲上不如后者,但它和德国著名的“追猎者”有相似之处。悬挂系统同样取自T-70---每5个负重轮和4个托带轮就有一个独立的扭杆。 The hull was made of rolled armor plates of varying thickness, from 10mm to 35mm – only the frontal armor had a significant slope in order to make it easier for the crew to operate the vehicle by giving them enough space. The vehicle had a crew of four – driver, commander, gunner and loader. The frontal plate had a massive hole cut in it in order to mount the powerful 76,2mm S-1 gun. The gun itself had a -5/+14 depression/elevation and could traverse 13,5 degrees to each side. The gun mount resembled the SU-76I gun mount for the same gun. The vehicle, as stated above, was powered by the GMC-71 engine, locally produced under the designation of YAZ-206. 车体由厚度从10-35mm不等的轧制钢板制成,仅有前装甲有着很大的倾角---这是为了给车组留出足够的空间操纵坦克。车组共4人,驾驶员,车长,炮手和装填手。为了安装这门威力巨大的76.2mm S-1炮,在前装甲上开了一个大洞。火炮的俯仰角为-5-+14度,左右射界均为13.5度,炮座和SU-76I的类似。国产化的GMC-71引擎又被称作YAZ-206,用于驱动该坦克。 The vehicle was built in one prototype, that was designated SU-74 or SU-76-I. It passed succesfully both factory and army trials. However, it was already second half of 1943 and the Soviets were meeting heavily armored German tanks, such as the Panther and the Tiger – the gun was considered too weak to knock out the German behemoths at that point and it was this that caused this vehicle not to be mass-produced. The entire IT (tank destroyer) series of light “Hetzer-like” series, that started much earlier, was in fact a Soviet (at first desperate) attempt to bring more AT guns to the field to compensate for the lack of AT measures and tanks, but in 1943, the danger of being overrun by German Blitzkrieg was no longer present. 建造了一部原型车,代号SU-74或是SU-76-I,并成功的通过了工厂和军队的审查,不过这个项目出现的时间已经是在1943年下半叶了,那时苏联人在正面临着来自以虎豹为代表的德国重装甲的威胁。S-1炮面对这些钢铁巨兽显得尤为无力,这也是这坦克没能投入量产的原因。开始时间较早的整个IT(俄语的坦克歼击车缩写)项目,即苏联“追猎者”的起源,实际上是毛子为了将更多的反坦克炮搬上战场的一个应急之举,主要是为了解决前线部队缺乏反坦克手段以及坦克部队的问题。但是在1943年,苏联被德国闪电战所击垮的可能性已然变为了0。 Despite this setback, GAZ continued its work on the light tank destroyer series (despite the apparent obsolescence of the concept, that – ironically – started to appeal to Germans in turn, as they met more and more Soviet armored vehicles). In Summer 1943, the production of 57mm ZIS-2 guns was resumed in the Gorky Artillery Plant No.92. These guns had pretty good ballistic characteristics and GAZ decided it wouldn’t be such a bad idea to actually use a high-power 57mm gun in the GAZ-74 chassis to produce a better-performing tank destroyer. They introduced more variants of the project – one was to be equipped with the 57mm gun (S-1-57, ZIS-4) and the other with some sort of improved 76mm (S-54 presumably). The 57mm variant recieved the designation of SU-57b. 除开上面提到的这个问题,GAZ继续开发着轻型坦克歼击车(虽说这个概念已经过时了,反倒是德国人用起了这个概念以对抗苏联的钢铁洪流)。1943年夏,高尔基炮兵工厂92号厂恢复了57mm ZIS-2炮的生产工作。该炮的弹道性能很出色,GAZ决定在GAZ-74底盘上装备该炮以创造出性能更佳的坦克歼击车。他们为这个项目开发出了更多型号,其中之一就装备了57mm炮(S-1-57,ZIS-4)以及某种改进型号的76mm炮(似乎是S-54)。装57mm炮的型号得到了SU-57b的代号。 The vehicle was built on the SU-76D chassis, only the gun was replaced with 57mm ZIS-4. According to Soviet data, this gun could penetrate 90mm at 1000 meters and 100mm at 500 meters (90 degrees). 该坦克基于SU-76D的底盘建造,仅有主炮被替换为57mm ZIS-4。根据苏联方面的数据,该炮能够在1000m距离上击穿90mm的垂直装甲,500m击穿100mm垂直装甲。 A prototype was built as well and it passed all the required tests, but, just like the project before, it was not accepted in service. The reasons for the cancellation of the project was – apart from what was stated above – that the vehicle was actually expensive to produce. 同样也造出了一个原型,通过了所有需要参加的测试,但是和前面的项目一样,它没能被军方接受。原因,除了上面提到的之外,还有就是造价太高。 The development of the GAZ-74 chassis ended in 1944 with the introduction of the improved version, carrying a 76mm gun (S-1), but with improved armor (60mm in the front). This vehicle was designated SU-76D (or GAZ-76D). A prototype was built and was tested by the army under the designation of SU-80. However, at this point, the SU-76M was already produced in massive numbers and it was preferred by the army to keep the mass-produced vehicle instead of introducing a completely new one. GAZ-74底盘的开发工作一直持续到1944年才结束,最终搞出了一个改进型号,同样携带一门76mm S-1炮,并将正面装甲加强到了60mm。该车代号为SU-76D(或者GAZ-76D)。造出了一部原型车,并以SU-80的代号接受了军方的测试。但是这个时候SU-76M已经大规模量产了,比起重新引入一个新的设计量产,军方自然更偏好保持现状。 The SU-76D emerged one more time in early 1945 – in Hungary, the vehicle was tested against a captured Hetzer along with the SU-57b with mixed success (one of the listed SU-57b drawbacks was the lack of powerful HE shells for example). SU-76D与1945年早期再次出现---在匈牙利,军方用这车和SU-57b对追猎者进行了射击测试,测试结果有好有坏(记录在案的SU-57b的一个缺点就是缺乏威力足够的高爆弹药)。
SU-74 乘员: 4 重量: 11,6 tons 引擎: GMC-71柴油机(110hp) 推重比: 9,5 hp/t 极速: 36 km/h 车体装甲: 35/15/15mm 战斗室正面: 35mm 主炮: 76mm S-1 最大射速: 20 RPM 战斗射速: 15 RPM 载弹量: 71
SU-57b 乘员: 4 重量: 9,56 tons 引擎: ZIS-16 (100hp) 推重比: 10,5 hp/t 极速: 40 km/h 车体装甲: 25/15/15mm 战斗室正面: 25mm 主炮: 57mm ZIS-4 最大射速: 20 RPM 战斗射速: 15 RPM 载弹量: 72
SU-76D 乘员: 4 重量: 11,6 tons 引擎: GMC-71 diesel (110hp) 推重比: 9,5 hp/t 最大速度: 36 km/h 车体装甲: 60/15/15mm 战斗室正面: 60mm 主炮: 76mm S-1 最大射速: 20 RPM 战斗射速: 15 RPM 载弹量: 71 [编辑:不详]
|
本资讯及文章仅代表发表厂商及作者观点,不代表叶子猪本身观点!